Common STIs, how they are spread, and how harmful they are.
BACTERIA |
VIRAL |
PROTOZOAL |
FUNGAL |
PARASITIC |
Gonorrhoea (Neisseria gonorrhea.) |
HIV |
Trichomoniasis (Trichomonas vaginalis.) |
Candidiasis (Candida albicans) |
Pubic lice *Passed on by close body contact and not by actual penetration. |
Syphilis (Treponema pallidum.) |
Genital warts (HPV) |
|||
Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis.) |
Hepatitis B (HBV) |
|||
Chanchroid (Haemophilus ducreyi.) |
Genital herpes (Herpes Type 2) |
Gonorrhoea
- It is a sexually transmitted bacterial infection affecting the cervix, urethra, throat and rectum.
- It can cause pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility in women and severe inflammation of the urinary tract in men. If the mother is infected at the time of delivery, it can cause blindness in the baby.
- It can be treated with antibiotics, however, long term complications may not be reversible.
Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is a type of viral infection that affects the liver. It can cause cancer and even death.
- It is transmitted through sex, and also bodily fluids such as blood.
- Hepatitis B can be prevented by getting the Hepatitis B vaccine, It is safe and effective.
- Hepatitis vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth, children up to 18 years and adults who are at high risk for infection due to their occupation.
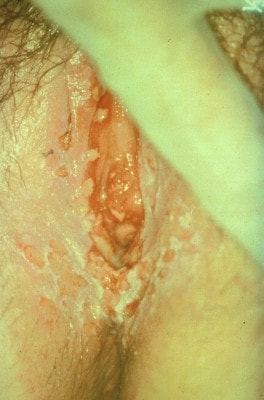
Syphilis
|
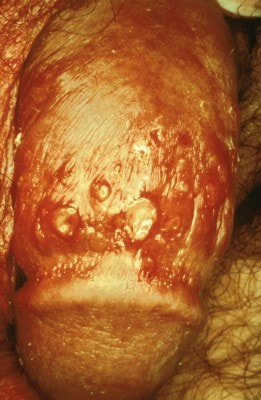
Genital Warts
- Genital warts are tiny growths on the skin around the genitals and anus. They are caused by certain types of viruses called human papilloma virus (HPV). HPV can be transmitted by sexual intercourse and also by touching- so condoms do not give 100% protection.
- Most HPV infections have no symptoms, but some cause warts that are painful and can bleed or discharge pus.
- Some types of HPV cause cervical cancer. A vaccine is available to protect against a few of the common cancer causing types. The vaccine however, does not protect against all types of HPV.
Chlamydia
- Chlamydia is one of the most common STI. It is a highly contagious sexually transmitted bacterial infection.
- Unfortunately most people are asymptomatic and do not have symptoms. Sometimes it causes unusual discharge, bleeding or pain during passing urine. For men, testicular pain sometimes occurs.
- It can cause problems in the reproductive organs and infertility. It can be treated with antibiotics, however, long term complications may not be reversible.
Herpes
|
HIV/AIDS
- HIV refers to the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It is a virus that destroys the white cells (our body’s immune system) making us vulnerable to infections and common illness.
- AIDS refers to Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome: AIDS is a consequence and the final stage of a HIV infection. Not everyone with HIV will develop AIDS. HIV can spread through:
- body fluids (semen and blood),
- through unprotected sexual intercourse,
- sharing needles (eg intravenous drug users)
- receiving contaminated blood products
- from mother to child during pregnancy
- using unsterilized instruments (e.g. tattoo pen, skin piercer)
- HIV is not spread by kissing, touching, sneezing, using the same plates and spoons or coughing. It is not spread by sitting on toilet seats, drinking from water-fountain, swimming in common swimming pools, showers or though insect bites.
- Understanding how HIV is transmitted will go a long way into fighting the stigma of this disease.
- While there is no cure for HIV or AIDS, the disease can be well managed by certain medication. Taking medication extends the lifespan of infected individuals. These medicines must be taken every day.
Does an HIV infected person have symptoms?
- Symptoms of HIV infection can be very vague during the early stage, such as having flu-like symptoms (rashes, chills, night sweats, sore throat, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and mouth ulcers). Just by having these symptoms and being sexually active does not mean one have HIV. The only way to confirm infection is by undergoing specific blood test for HIV.